CBD vs. THC: The Basics
Navigating cannabis terms can feel a lot like alphabet soup. CBD? THC? CBG? THCA? Isn't it all weed?
Yes, and…
Understanding these subtle differences is vital for creating a conscious relationship to plant medicine.
For this post, I'll focus on the leading players – CBD and THC.
Notice the chemical structure of CBD and THC are nearly identical! Both are made up of 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms, with a slight difference in their arrangement — this leads to slightly different effects.
Image: CBD Central
You've probably noticed that CBD has taken over the wellness and cannabis industries, as it is the "more legal and socially accepted" component of the cannabis plant.
However, CBD is just one of the many hundreds of compounds – called cannabinoids – that make up this magical medicine. Stay tuned for a future post on cannabis terminology, where we will dive deep into the cannabinoids about which you may not know much.
First, a little bit of science and history...
BOTH CBD and THC are considered cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that can fall into one of 3 categories: endogenous (from inside the body) cannabinoids, phytocannabinoids (produced by the plant), and synthetic cannabinoids. So, CBD and THC (plus CBG, CBN, and many others) are phytocannabinoids.
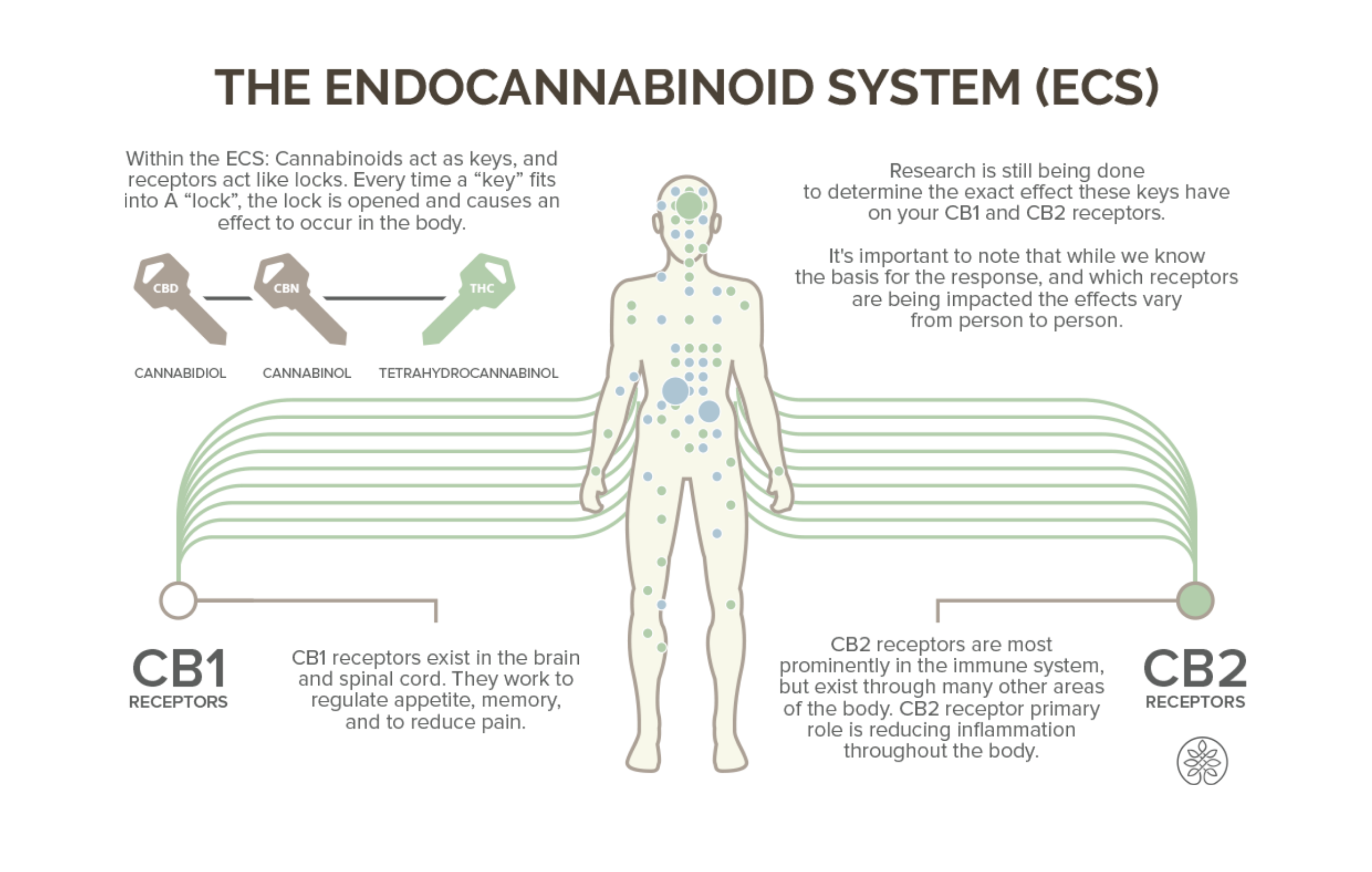
Cannabinoids bind to and activate receptors throughout the body, which comprise the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). The ECS primarily exists to maintain homeostasis (balanced functioning) in the body. This system is a whole other topic, but it is helpful to understand that cannabinoids and the ECS act like a lock and key, and the ECS exists naturally in the human body.
A basic overview of the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Image: Hempure
In 1963, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam and his team at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem isolated CBD, and in 1964, they isolated THC. While this has been groundbreaking research, the tendency to see each cannabinoid in isolation -- rather than a part of a holistic ecosystem -- has continued. (Stay tuned for a future blog post on the "entourage effect.")
CBD stands for cannabidiol, and it has become the "star" of cannabis in the wellness industry.
Despite being seen as a weaker compound that won't "get you high," CBD itself has a range of reported therapeutic benefits. It is anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic (relieves anxiety), antidepressant, anti-nausea, antioxidant, and neuroprotective (protects brain cells), among other healing properties. Interestingly, despite not being as psychoactive as THC (CBD is psychoactive, because it affects the brain and contributes to changes in mood, awareness, feelings, thoughts and behavior), some people may report feeling "altered" after using CBD, which speaks to how normalized chronic low-level anxiety is in most people.
Because of prohibition and the resulting "illicit market," a desire to achieve the highest levels of THC has led to CBD being "bred out" of most marijuana strains.
In 2018, the FDA approved CBD for use in the drug Epidiolex, which treats seizures. The irony is that cannabis is still listed as a "Schedule 1" drug (this category includes heroin and is "worse" than categories for drugs like oxycodone and cocaine), which (falsely) suggests it has no medical benefits and has a high potential of abuse. Additionally, the U.S. federal government did patent the medical benefits of cannabis in 2003 (Patent No. 6,630,507).
Knowing the history of cannabis and the racist, gaslight-y context in which it continues to exist is a necessary part of developing a conscious relationship with this plant. For more discussion around this context, listen to the first episode of Conscious Kush Conversations, where we dive into some of these complex dynamics.
Bottom line: Your body knows the truth, even if the government/other people/media try to convince you otherwise.
Like CBD, THC (also known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) can offer many similar healing benefits, including being anti-nausea, anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving, and antidepressant. THC is also the most abundant of the cannabinoids found in cannabis and is what primarily contributes to the "high" or psychoactive, mind-altering effects we associate with weed.
It's important to note that people often call THC the "active" ingredient in cannabis; however, this is untrue and highlights the power of language in reinforcing certain beliefs. What is true is the cannabinoids all work together to provide a range of physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual benefits.
One of the coolest things about how THC and CBD relate to one another is that CBD has been shown to counteract the more “negative” side effects of THC, like getting too high or paranoid. Because of this, I always recommend having a CBD tincture handy when consuming THC, especially if you're a beginner — juuust in case you get a little too lit. But how cool is it that a single plant possesses the ability to alter and then rebalance its own effects??!
Nature is a genius, y'all.
There are so many amazing properties, cannabinoids, and terpenes to explore in the cannabis plant. Stay tuned for future educational posts! I'd also love to hear your thoughts on what resonates in the comments below.